He was born in 1914 on a farm in Iowa. In high school he was active in athletics, participating in football, baseball, and wrestling. His grandfather urged him to go to college after he finished high school. He attended the University of Minnesota and studied forestry. After graduation he went to work for the U.S. Forestry Service.
After hearing Professor Elvin C. Stakman at the University of Minnesota speak about plant diseases, Borlaug talked with him about pursuing an advanced degree in plant pathology.* He returned to school and got a masters degree and a doctorate in that field. Then he worked for a couple of years as a researcher for Du Pont.
A turning point in his career came when he accepted an appointment by the Rockefeller Foundation to work with the Mexican government improving the crops in Mexico. The wheat they were growing did not produce much grain and the tall stalks would fall over before they could be harvested.
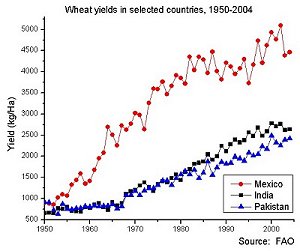
Through experimentation he was able to develop a dwarf wheat which was shorter and would not fall to the ground. This new wheat also made larger heads of wheat with triple the number of grains in each head.
Farmers could produce a much larger crop of wheat on the same ground they had been farming.
This variety of wheat was also not subject to disease that had plagued their crops before. It was a remarkable improvement!
They took this new wheat seed to India and Pakistan where there was a famine. People were starving to death. When the seed was planted in these countries they had similar results; a great increase in the amount of food the people were able to produce. There was more food for them to eat and more children were able to thrive and grow.
He also developed a new grain called triticale* which was part wheat and part rye. It produced a nutritious grain larger than wheat which could feed masses of people.
In order to spread this knowledge, Borlaug trained young scientists in many countries to carry on the work. He went into the fields with them and showed them the best methods for growing the grain.
By 1974 India was producing enough grain to feed the people of that country, and ten years later there was such an abundance they were even able to export some grain. (quote from an article by Gregg Easterbrook)
When people are able to plant high-yield grain crops, they can feed themselves using fewer acres of land. This helps to prevent more deforestation.* Instead of cutting down trees to make more farmland, they can grow a crop on the fewer acres they already have in production. The "slash-and-burn"* method where people cut down the forests has caused more soil erosion. Valuable land is washed into the sea, and sometimes windstorms carry the topsoil away. The loss of trees also affects the quality of the air we breathe.
Some environmentalists* have opposed Borlaug's methods and have tried to stop his work. They protest that using fertilizer is bad, though it only replaces the soil nutrients that have been depleted. Others are sure that bioengineered* food is toxic to people and will make them ill. They think people should continue using the same seed they have used for years. The new strains continue to grow wheat and rye for making bread, and these new varieties will produce even more grain than the old variety, and the shorter stalks will stand up until harvest.
Studies (of this type) have established that the level of safety to consumers of current genetically engineered foods is likely to be equivalent to that of traditional foods. At present, no verifiable evidence of adverse health effects of BD foods has been reported, although the current passive reporting system probably would not detect minor or rare adverse effects or a moderate increase in effects with a high background incidence such as diarrhea.
Are GMO Foods Safe?
Article from the New York Times
Why People Oppose GMO Foods
Roger Thurow, author of Enough: Why the World's Poorest Starve in an Age of Plenty notes that Africa was left out of the "Green Revolution" and as a result millions of Ethiopians face starvation just as they did 25 years ago.
Bill Gates has mentioned that the best way to reduce poverty and hunger in the developing world is through helping small farmers be as productive in growing as much food as possible.(quote from Roger Thurow in the Dallas Morning News)
Norman Borlaug taught and researched at Texas A and M University from 1984 until his death in 2009.
During his life he received many honors for his work, and in 1970 was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize. In 1977 he received the Presidential Medal of Freedom for his humanitarian contribution, and in 2007 he was awarded The Congressional Gold Medal.
"Some credit him with saving more human lives than any other person in history." -- Bruce Alberts, President of the National Academy of Sciences, USA
This biography by Patsy Stevens, a retired teacher, was written in 2009.


 A frequent question:
A frequent question: